Immediately After The Switch Is Closed What Is The Voltage Across The Capacitor | The switch is closed at t=o. If the switch is then connected upward, determine the charge on each capacitor after\ the switching. Circuit behavior described by kirchhoffs rules: (for each statement select t true, f false). Q is same as immediately before.
It the current is rapidly changing there is a lot of voltage, if the current is not. What is the current through the right resistor immediately after the switch 2 is closed? Immediately after the switch is closed, what is the potential difference across the inductor? Problem 2 20f 16 » constants immediately after the switch is closed, what is the voltage across the resistor? 6) after being closed a long time, switch 1 is opened and switch 2 is closed.
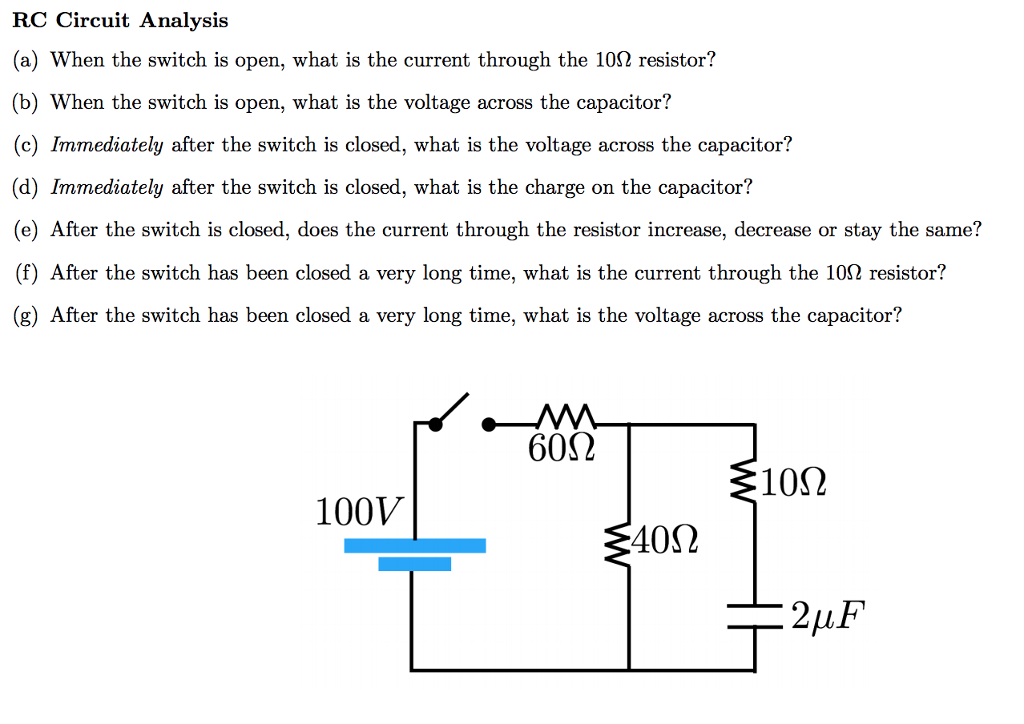
And we've been asked to find the potential difference across the capacitor immediately after the switch is closed. Homework statement the problem is: As soon as the switch is closed, current flows to and from the initially uncharged capacitor. Immediately after the switch is closed, the initial current is io =vo /r=10v/10ω. So immediately after closing the switch, the voltage over the capacitor can not change and therefore the voltage presented to the further right of your circuit is 0. Clockwise counterclockwise there is no current because the capacitor does not allow the current to pass through. Show your solution.) what you want to understand is that an inductor creates a voltage to resist sudden changes in current. The current in the capacitor can be thought of as a different sort of current, not involved with the answer: 6) after being closed a long time, switch 1 is opened and switch 2 is closed. 1 answer to the switch s in fig. Of course, when the charge of the capacitor is not changing, then there is no current. (c) what is the current in the inductor after the switch has been closed for a long time? Accordingly, the voltage across the 600 ohm resistor is also zero, since they are in parallel.
Immediately after the switch is closed, what is the potential difference across the inductor? So, initially, because this switch is open, there is no current running through the circuit. The resistor and inductor are in series the initial charge on the capacitor is zero. Show your solution.) what you want to understand is that an inductor creates a voltage to resist sudden changes in current. What is the output voltage immediately after the switch is closed?

Been closed, what is the voltage drop vc across the capacitor in terms of vb?show answer correct answer17% part (c) calculate the charge q on the capacitor a very long time after the switch has been closed in c.no attempt no initially, the capacitor is uncharged. 1 answer to the switch s in fig. (for each statement select t true, f false). Part b immediately after the switch is closed, what is the voltage across the resistor? What is the output voltage immediately after the switch is closed? The switch is closed at t=o. Immediately after the switch s1 is closed: What is the current through the right resistor immediately after switch 2 is what is the voltage across the capacitor after a long time ? Problem 2 20f 16 » constants immediately after the switch is closed, what is the voltage across the resistor? Just follow the hints to find the right answer and learn about capacitors as you go. Determine the current, i(t), when the capacitance is c = 0.125 f and the voltage is v(t) = 12 cos(2t + 30°) v. D acos(ωt +θ ) =− asin (ωt +θ ) ⋅ d (ωt +θ ). Clockwise counterclockwise there is no current because the capacitor does not allow the current to pass through.
Or is it a capacitor with an initial charge across it? At that point, the series capacitor would take its turn acting as an infinite impedance to the flow of current after instantly energizing a potential across itself. If the switch is then connected upward, determine the charge on each capacitor after\ the switching. D acos(ωt +θ ) =− asin (ωt +θ ) ⋅ d (ωt +θ ). Of course, when the charge of the capacitor is not changing, then there is no current.

Clockwise counterclockwise there is no current because the capacitor does not allow the current to pass through. The uncharged capacitor effectively shorts out that resistor, leaving the emf of 36 v across the 1.2 k. When the switch is closed to connect the battery to the capacitor, there is zero voltage across the capacitor since it has no charge buildup. When you switch a voltmeter from a lower to a higher voltage range, an additional resistor is added in series with the meter, increasing the voltage necessary to create the same voltage drop across or current flow through the. As soon as the switch is closed, current flows to and from the initially uncharged capacitor. D acos(ωt +θ ) =− asin (ωt +θ ) ⋅ d (ωt +θ ). What is the voltage across the plates of the capacitor if the capacitance is 10 uf and the charge stored is 30 uc? Voltage across c = voltage across r. So immediately after closing the switch, the voltage over the capacitor can not change and therefore the voltage presented to the further right of your circuit is 0. Consider a series circuit containing a resistor of resistance r and a capacitor of capacitance c connected to a source of initially, the switch is open and the capacitor discharged. Just after the switch is closed, the current in the circuit is 1. Current and voltage are linked by the resistance not the capacitance an uncharged capacitor of fixed capacitance is connected in series with a switch and battery. That should allow you to determine the voltage across the capacitor.
The capacitor is initially uncharged and switches s1 and s2 are initially open mmediately. 1 answer to the switch s in fig.
Immediately After The Switch Is Closed What Is The Voltage Across The Capacitor: Immediately after the switch is closed, the initial current is io =vo /r=10v/10ω.

Post a Comment